
The intracellular fluid compartment (ICF) refers to all fluid enclosed within cells by their plasma membranes. We can talk about body fluids in terms of their specific compartments, which are largely separated from one another by some sort of physical barrier. The Intracellular Fluid (Icf) Is The Fluid Within Cells. The IF is responsible for transporting materials between the plasma and the cells.
Blood plasma is the second component of the ECF. Interstitial fluid (IF) is part of the extracellular fluid (ECF) between cells. ICF, or intracellular fluid, is the fluid that resides in the cytoplasm of each body cell.įluid within cells is known as intracellular fluid (ICF). Extracellular fluid can also be found in blood vessels. There is fluid between each cell of the body called interstitial fluid (IF), which is a type of extracellular fluid (ECF). There are several cells surrounding a small blood vessel in this diagram. Fluid Compartments: Intracellular And Extracellular Fluid Teeth, on the other hand, contain the least amount of water, at 8–10 percent. The brain and kidneys have the highest proportion of water, which makes up 80-85 percent of their mass. A person’s percent of body water changes as he or she develops, since the proportions of each organ, muscle, fat, bone, and other tissue change from infancy to adulthood. Human beings are mainly composed of water, ranging from about 75 percent of body mass in infants to about 50–60 percent in adult men and women, and as low as 45 percent in those over 65 years of age. Water Content Varies In Different Body Organs And Tissues, From As Little As 8 Percent In The Teeth To As Much As 85 Percent In The Brain.
BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS PERCENTAGES SKIN
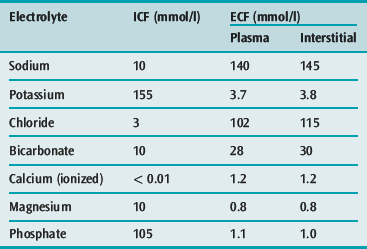
There is typically 80% to 85% water in the brain, teeth contain 8% to 10% water, a single lung contains 75% to 80% water, the heart contains 75% to 80% water, the bones contain 20% to 25% water, the liver contains 70% to 75% water, the kidneys contain 80% to 85% water, the skin contains 70% to 75% water, and the muscles also contain 70% to 75% water. Each organ contains a specific percentage of water. Body Water ContentĪ silhouette of a human body with various organs highlighted is depicted in this illustration. Maintaining a balance of solutes inside and outside of cells is necessary to ensure normal cell function. Consequently, water will move into and out of cells and tissues based on the relative concentrations of water and solutes found there. Water diffuses from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration along an osmotic gradient across a semi-permeable membrane by osmosis. Osmosis is the process of water moving between compartments in the body by passing through semipermeable membranes of cells. Sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl–) are commonly referred to as electrolytes. It is common in medicine to refer to a mineral dissociated from a salt that has an electrical charge (an ion) as an electrolyte. In the body, solutes vary depending on the part of the body but can include proteins that transport lipids, carbohydrates, and, very importantly, electrolytes. Solutes are substances dissolved in a solution.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
